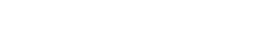|
| |
|

By Petroleum Technology Transfer Council |
Horizontal drilling increases production in a reef formation
At a modest added cost, this drilling program more than tripled production and increased ultimate recoverable reserves in this Michigan Niagaran Reef
Christopher Wood, Traverse City, Michigan
In 1992, SOMOCO Inc. – a Michigan-based company – initially developed the Novi 29 Niagaran reef by drilling a 35° directional discovery well into the southeast corner of the reef. Some eight years later, to increase production and access additional reserves, the well was re-entered, drilling a 417-ft horizontal lateral with a second 272-ft horizontal spur. For a re-entry cost of only $175,000, production more than tripled and estimated ultimate recoverable reserves increased by 233,000 barrels of oil and 606 MMcf. A second horizontal well was subsequently drilled into the north end of the reef. Combined, the incremental reserves attributed to horizontal development are estimated at 283,000 barrels of oil and 1,240 MMcf.
CASE STUDY
The Niagaran Reef in Oakland Co., Michigan, underlies the Novi 29 Unit and is located on the southeast edge of Niagaran shelf development in Michigan. Portions of the 165-acre reef underlie a subdivision and non-developmental wetlands, thus the need for a directional discovery well. Commerce Bank Trustee (CBT) 1-29 was drilled from the northwest to southeast, Fig. 1. CBT 1-29 was held at 35° as it went through the reef. Initial production from the Brown Niagaran oil zone and underlying bitumen zone was about 150 bopd. By 1998, production had declined to about 60 bopd. An acid frac increased production some 20 bopd, but production was back down to 60 bopd by mid-2000. With this completion, ultimate recoverable reserves were estimated at 358,000 barrels of oil and 109 MMcf.
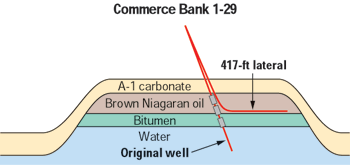 |
Fig. 1. The original Commerce Bank 1-29 well and lateral, in cross-section.
|
|
In 2000, SOMOCO re-entered the well to drill a 417-ft horizontal lateral with an additional 272-ft horizontal spur in the Brown Niagaran zone, Fig. 1. The eight-day re-entry workover cost was $175,000. Both the main lateral and the spur were individually stimulated with 2,000 gallons of HCl. Production increased to about 200 Bopd – more than three-fold – and held relatively steady through early 2002, Fig. 2. Ultimate recoverable reserve estimates were increased to 591,000 barrels of oil and 715 MMcf.
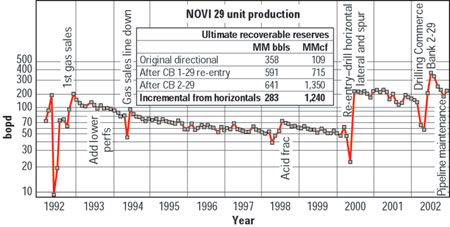 |
Fig. 2. Oil production history from 1992 to 2003. Adding lower perforations did not help, but drilling of horizontals in 2000 and 2002 did.
|
|
Some disruptions in production occurred as a second horizontal, CBT 2-29, was being drilled to drain reserves on the northern edge of the reef during 2002, Fig. 3. With both horizontals, production exceeds 250 bopd. Ultimate recoverable reserves from the Novi 29 Unit are now estimated at 641,000 barrels of oil, nearly double those of the original directional well. Gas reserves increased more than 10 times that of the original well, to 1,350 MMcf.
 |
Fig. 3. The Commerce Bank 2-29 directional/ horizontal well (top). Cross-section (top) and structural schematic (bottom).
|
|
Acknowledgment
The author thanks SOMOCO Inc., of Traverse City, Michigan, for permission to publish this article.
THE AUTHOR
|
| |
Christopher Wood is an independent petroleum engineering consultant working the Michigan basin. His 25 years of experience covers many areas, including prospect generation, well completion, and production and reservoir economics. He earned a BS degree in geology from Illinois State University in 1976 and an MS degree in geological engineering from University of Missouri-Rolla in 1978. Email: corsair23@aol.com
|
| |
|
|