Technology at Work: Multilateral wells provide deepwater solutions
Feb. 2002 Vol. 223 No. 2 Feature Article TECHNOLOGY AT WORK Multilateral wells provide deepwater solutions Finding cost-effective, fit-for-purpose recovery
TECHNOLOGY AT WORKMultilateral wells provide deepwater solutionsFinding cost-effective, fit-for-purpose recovery solutions is imperative to safe, economic development of high-cost / high-risk deepwater fields. As proven by their track record, multilateral (ML) wells hold the potential to provide these solutions. A multilateral well is started somewhere in the world almost every day – quite an accomplishment, considering that the technology is barely a decade old and has become commonplace only recently. Baker Oil Tools has developed and applied ML well technology for about a decade and has pioneered low-risk solutions such as the Level 3 Hook Hanger and Level 6 Formation Junction and Splitter systems. Throughout this time, the company has tracked the relative cost, production and revenue of ML vs. conventional-well solutions. The results have been impressive. In Venezuela, for example, Level 3 Hook Hanger systems have yielded up to 900 bopd additional production per well, in a comparison of 23 multilaterals, vs. 108 single wells. The cost of these ML wells has averaged 1.58 times that of a single well. Per-day increase in revenue at $20/bbl has been as much as $18,000 per well. TAML levels reviewed. To provide a consistent comparison of ML systems industry wide, a classification system was developed by TAML (Technology Advancement for Multilaterals), a consortium group comprising operators and service companies. The classification system divides wells into "levels" depending on junction functionality. Based on these definitions, only Levels 5 and 6 provide pressure integrity at the junction. Level 5 completions use a complex configuration of packers to isolate the junction and provide pressure integrity. Level 6 completions are much simpler in design and implementation. Levels 1 through 4 do not provide pressure integrity at the junction, and of these, only Levels 3 and 4 provide mechanical support at the junction. Introduction of the Hook Hanger system marked a significant step in development of cost-effective, fit-for-purpose ML solutions, since it offered the option for re-entry into both the lateral and the main bore. Prior to this development, Level 3 systems provided little functionality since a liner anchored back to the main bore limited re-entry to only the lateral. As a result, achieving re-entry into both the lateral and main bore required moving up to a higher-complexity, higher-cost TAML level. Level 3 solutions have become increasingly popular with the new option.
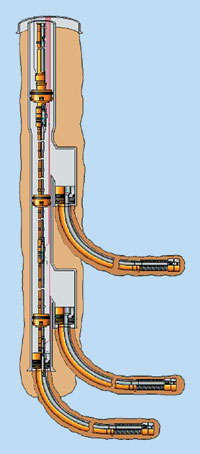
Meeting deepwater challenges. Among deepwater completion challenges that must be addressed by ML systems are: high burst and/or collapse pressure requirements for the casing or liner; high cost of well re-entry; and need to manage wellbore production. To meet these challenges, some Level 6 systems, including Baker’s high-pressure splitter systems, have been designed to withstand burst and collapse pressures greater than 10,000 psi. Similarly, completion companies have designed intelligent well systems that can be configured with a Level 6 ML to provide the operator with significant cost savings and wellbore management solutions. The company has proposed at least one such system for a deepwater application in the coming year, as shown in the accompanying illustration. Improving deepwater economics offshore Brazil. With 73% of its current oil/gas equivalent reserves and an estimated 60% of all future reserves located beneath deep, 1,300 – 3,280-ft (400 – 1,000-m) and ultra-deep, >3,280-ft water, Brazilian operator Petrobrás is committed to advancing technologies such as multilateral wells that enable safe, cost-effective development of deepwater reserves. Recently, Petrobrás and Baker completed the fifth deepwater ML well that met all of Petrobrás’ objectives. These wells were professionally designed and managed, then implemented from a semisubmersible rig. They included both injectors and producers. In both cases, multilateral technology provided significant positive impact on overall field economics by allowing the operator to use a low-risk, cost-attractive solution for optimizing reservoir management. Throughout the project, the cost of an ML well has averaged 1.43 times that of a single well, while increased production, revenues and savings have amounted to as much as $10 million over conventional technology applied in the region. Level 6 – not just for extreme applications. During an ML screening process, an operator may perceive – based on current lifting costs and expected future production – that a particular project requires only a mechanically supported junction and does not justify an "exotic" pre-manufactured junction system. However, many operators are beginning to realize that Level 6 junctions, once considered exotic, actually offer a low-risk, highly flexible and economic solution that is applicable in both traditional Level 3, economically weighted environments, as well as in higher-cost, higher-risk Level 5 environments. Therefore, Level 6 junctions are no longer considered only for extreme applications, but instead are being pursued more widely as methods of achieving a mechanically and hydraulically sound junction without the high associated risk of previous ML systems. The Level 6 process of pre-manufacturing the junction and then installing it in the wellbore significantly reduces risk, while enabling high-pressure junction capabilities and flexible completion options. Many operators who have seen the benefits of using this advanced multilateral technology to effectively manage fluid movement within a variety of reservoirs are now looking to apply it in technically challenging deepwater environments. Numerous Level 6 ML wells are planned for deepwater installations in 2002; and in the future, Level 6 ML systems likely will be applied in deepwater developments on a daily basis. |
- X80 heavy wall pipe solutions for deep/ultra-deepwater field developments in mild sour environment (November 2023)
- Wellbore seal control and monitoring enhance deepwater MPD operations (October 2023)
- Novel approaches to deepwater steel catenary production riser life extension benefit ESG (September 2023)
- Advancing casing drilling to deepwater: Rethinking top hole well construction (August 2023)
- Regional Report: Guyana-Suriname (July 2023)
- Oil States’ Taylor sees pick-up in OFS business in deepwater and international sectors (June 2023)
- Applying ultra-deep LWD resistivity technology successfully in a SAGD operation (May 2019)
- Adoption of wireless intelligent completions advances (May 2019)
- Majors double down as takeaway crunch eases (April 2019)
- What’s new in well logging and formation evaluation (April 2019)
- Qualification of a 20,000-psi subsea BOP: A collaborative approach (February 2019)
- ConocoPhillips’ Greg Leveille sees rapid trajectory of technical advancement continuing (February 2019)